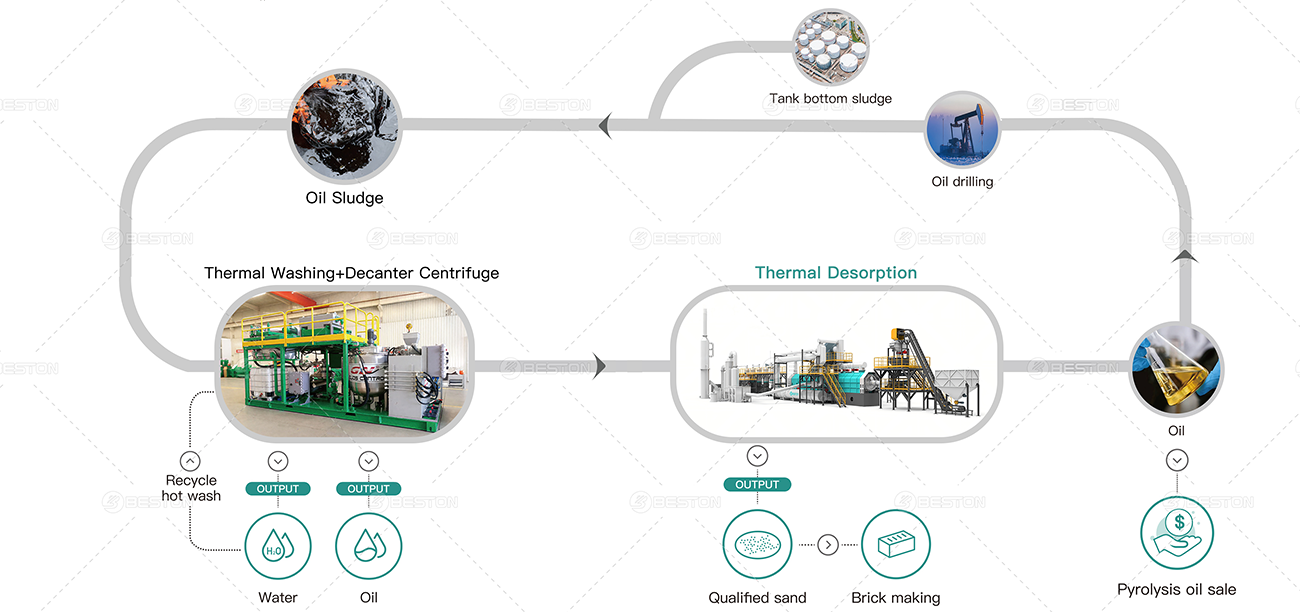
New Paragraph









Beston Group
Web: https://bestonmachinery.com/.
Email: sales@bestonmachinery.com
Egg Tray Making Machine
Web: https://bestoneggtraymachine.com/.
Email: sales@bestoneggtraymachine.com.
New Paragraph









https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-production-equipment/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/sawdust/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/palm-kernel-shell/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-production-equipment/reactor/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/videos/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/faqs/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-production-equipment/reactor/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biomass-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/components/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/price/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-production-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/coconut-shell/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/rice-hull/
https://bestonmachinery.com/wood-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/jute-stick/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/bamboo/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/sugarcane-bagasse/
https://bestonmachinery.com/coconut-shell-charcoal-making-machine-price/
https://bestonmachinery.com/shisha-charcoal-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/wood/
https://bestonmachinery.com/carbonization-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-manufacturing-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-production-equipment/mobile/
https://bestonmachinery.com/products/
https://bestonmachinery.com/straw-charcoal-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/solutions/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-machine-for-sale/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biomass-carbonization-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/carbonization-furnace/
https://bestonmachinery.com/carbon-sequestration-and-emission-reduction-solution/
https://bestonmachinery.com/soil-remediation-and-improvement-solution/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biomass-charcoal-as-fuel-alternative-for-industries/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pulp-moulding-products/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-for-sale/
https://bestonmachinery.com/bbq-charcoal-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/continuous/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biochar-pyrolysis-equipment/
https://bestonmachinery.com/biomass-charcoal-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/sewage-sludge-carbonization-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine/small/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-cameroon/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-cote-divoire/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-morocco/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-kenya/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-south-korea/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-thailand/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-ghana/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-the-philippines/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-sri-lanka/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-turkey/
https://bestonmachinery.com/charcoal-making-machine-in-the-united-states/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/continuous/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/reactor/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/plastic-to-fuel-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/faqs/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/mini-skid-mounted/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/manufacturer/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-pyrolysis-plant/project-report/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/cost/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/videos/
https://bestonmachinery.com/oil-sludge-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/mobile/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-to-oil-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-to-oil-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/rubber-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/technology/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/process/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/small/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-to-fuel-recycling-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/thermal-desorption-unit/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/components/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/semi-continuous/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-system/
https://bestonmachinery.com/plastic-pyrolysis-plant/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-morocco/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-machine-in-egypt/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-zimbabwe/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-australia/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/uk/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/the-philippines/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/nigeria/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/malaysia/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-canada/ https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-china/ https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-pyrolysis-plant-in-uae/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-morocco/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-machine-in-egypt/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-zimbabwe/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-australia/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/uk/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/the-philippines/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/nigeria/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant/malaysia/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-canada/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-china/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-pyrolysis-plant-in-uae/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-pakistan/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-botswana/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-plant-in-indonesia/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pyrolysis-oil-as-fuel-alternative-for-industries/
https://bestonmachinery.com/oil-contaminated-soil-remediation-solution/
https://bestonmachinery.com/tyre-shredder/
https://bestonmachinery.com/industrial-packaging-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine-in-saudi-arabia/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine-in-morocco/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine-in-russia/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/philippines/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/china/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/price-in-india/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/turkey/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/nigeria/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/price/
https://bestonmachinery.com/apple-tray-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/videos/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/dryer/
https://bestonmachinery.com/turnkey-project/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/project-report/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-packing-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/paper-tray-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/manual/
https://bestonmachinery.com/pulp-molding-machine/manufacturers/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-crate-making-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-manufacturing-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/for-sale/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-carton-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine-in-egypt/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine-in-iraq/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/india/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/pakistan/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/philippines/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/china/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/price-in-india/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/turkey/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/nigeria/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-box-machine/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/800-1000/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/1200-1500/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/2000pcs/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/2200-2500/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/3500-4500/
https://bestonmachinery.com/egg-tray-making-machine/5000-5500/